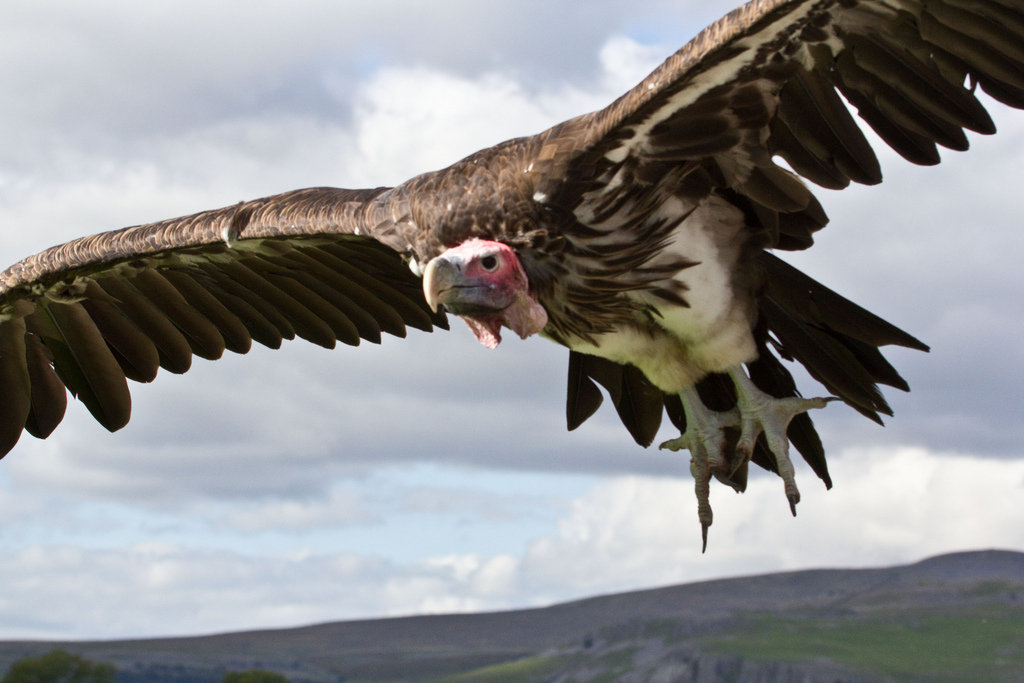


Researchers have been instructed to carry out periodic population analysis of the birds to monitor the trend across different states. Further, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change under the Government of India launched an Action Plan for Vulture Conservation that aims to prevent extinction of the species. Alternative options were proposed to be used for treatment amongst cattle. The frightful decline in vulture populations led to the ban of the drug diclofenac from being used by veterinarians in 2008. Superstitious beliefs have threatened them as well - locals residing in the Bundelkhand area of Northern India are known to use vulture eyes for tracing hidden treasures, and their eggs for black magic to bring the dead back to life.Ī Himalayan griffon was found drowning in the Yamuna river. Other factors that have contributed to the declining numbers include loss of habitat, retaliatory poisoning, agricultural practices, and illegal poaching for consumption. When the scavengers fed on livestock carcasses, they were exposed to diclofenac which led to their kidney failure. The main reason for this nosedive was found to be diclofenac, an anti-inflammatory drug used to treat farm animals. It is estimated that all populations are plummeting at an annual rate of 50 percent across India, Pakistan, and Nepal. Between 19, the population of these species declined by almost 99.9%. A notable study by a researcher of Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) documented that since the early 1990s, three species have seen a drastic decline in their numbers - White-rumped vulture, Indian vulture, Slender-billed vulture. Until the 1980s, vultures were a common sight across the country. The scavengers are highly threatened due to various factors. Hence, their importance is not only limited to ecology, but also extends to human society. These birds effectively prevent the need for any human interference when it comes to disposing carcasses of livestock. Simply put, an ecosystem can be considered healthy due to the presence of these scavengers. Carrions have now become a source of food for several rats and packs of feral dogs, who are both carriers of various diseases. With the decline of populations in India, it has been observed that carcasses that were consumed effectively by these birds now lie rotting for much longer.

They keep ecosystems in check and control any spread of diseases. By scavenging and consuming animal carcasses, vultures are known to be proud members of nature’s cleanup crew. Social and Ecological ImportanceĪ decaying carcass may cause several ailments such as brucellosis, tuberculosis, foot-and-mouth disease, and anthrax. Examples of such species in North America are black bear ( Ursus americanus), grizzly bear ( Ursus arctos), and wolverine ( Gulo gulo).All species share some common features such as large wings and keen eye sight. Scavengers, eating dead animals when they can find them. The turkey vulture ( Cathartes aura) of the Americas is one of the only bird species that has a sense of smell, which is utilized to find carrion. Some birds are specialized as scavengers, most notably the New World vultures (family Cathartidae) and Old World vultures (family Accipitridae).

Many marine crustaceans are important scavengers, including most species of crabs and gammarids. Invertebrates are the most abundant scavengers in terrestrial ecosystems, especially earthworms and insects such as beetles, flies, and ants.
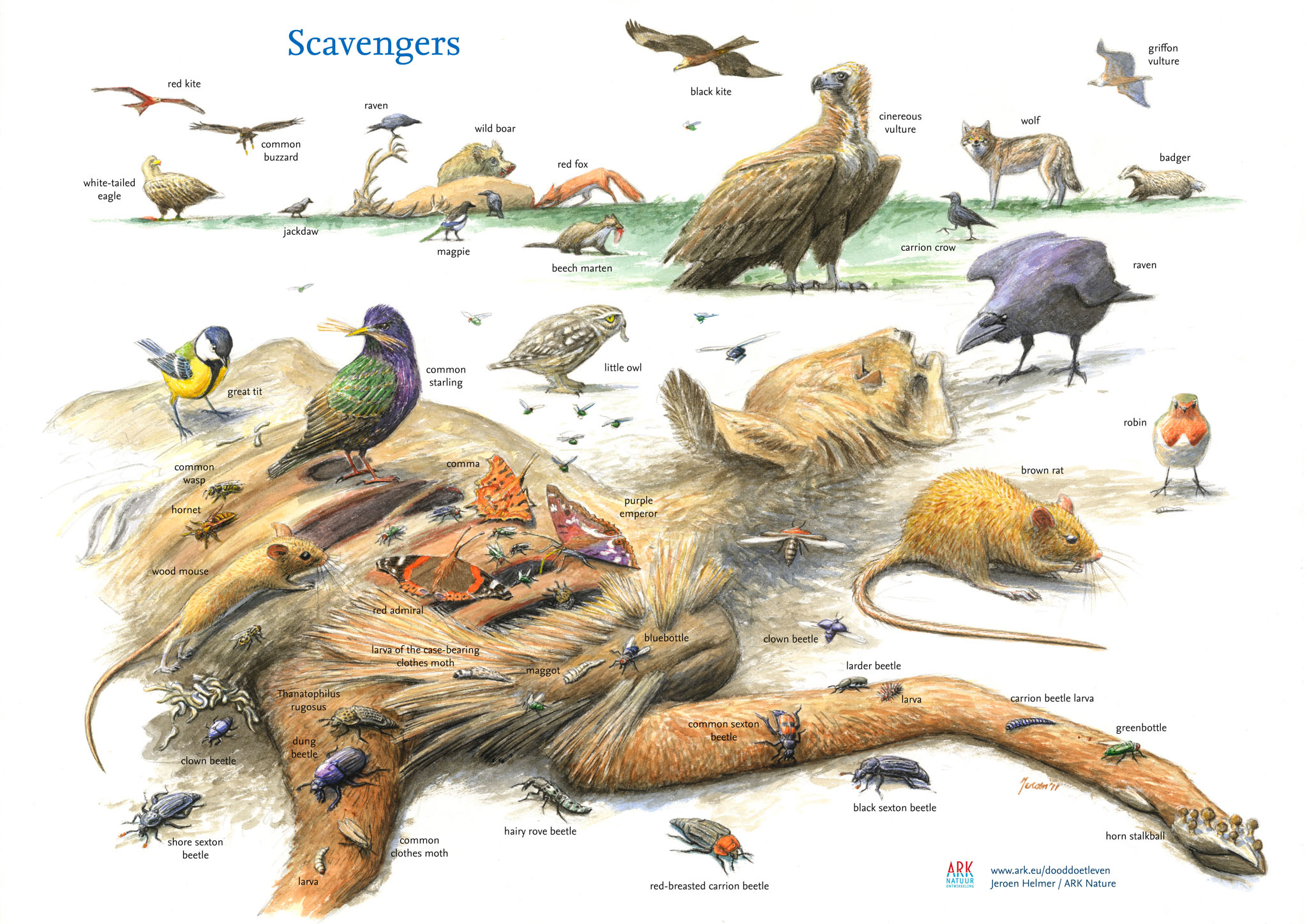
However, scavengers are important in the initial stages of biomass decomposition and recycling. The valuable ecological service of recycling of dead biomass is not just performed by scavengers-other detritivores such as bacteria, and fungi are also important, and in fact are largely responsible for the final stages of the decomposition and humification process. Excessive accumulations of dead plants can also bind up much of the nutrient capital of ecosystems, so that not enough is recycled for use by living plants, and ecosystem productivity becomes constrained by nutrient limitations. A similar effect can be caused to living plants by dead plant biomass. Large quantities of dead animal biomass can represent a indirect health hazard to living animals, by enhancing the survival of pathogens. Scavengers provide a very important ecological service, because they help to rapidly reduce dead animals and plants to simpler constituents, and thereby prevent an excessive accumulation of dead biomass. Scavengers are part of the detrital food web of ecosystems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
